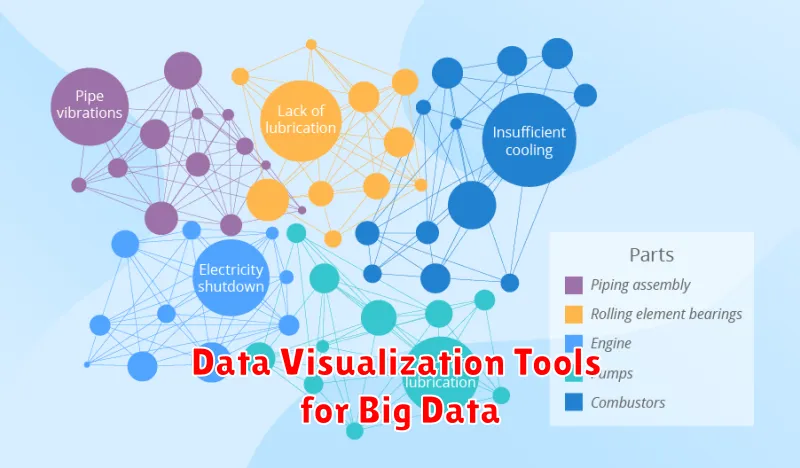
In today’s data-driven world, big data presents both immense opportunities and significant challenges. The sheer volume, velocity, and variety of data generated by modern systems can be overwhelming. Effectively analyzing and interpreting this big data is crucial for extracting actionable insights and making informed decisions. Data visualization tools play a pivotal role in transforming complex datasets into easily understandable visual representations, unlocking the power of big data and enabling organizations to gain a competitive edge. Selecting the appropriate data visualization tool for your specific needs is paramount, considering factors such as the type of data being analyzed, the desired level of interactivity, and the specific analytical goals.
This article explores the landscape of cutting-edge data visualization tools designed specifically for handling big data. We will delve into the features, capabilities, and strengths of various prominent tools, empowering you to choose the optimal solution for your data visualization needs. Understanding the diverse array of available data visualization tools and their applications is essential for harnessing the full potential of your big data and transforming raw information into actionable knowledge. From interactive dashboards and dynamic charts to geospatial visualizations and network graphs, data visualization provides the key to unlocking the hidden stories within your big data.
What Is Data Visualization?
Data visualization is the graphical representation of information and data. By using visual elements like charts, graphs, and maps, data visualization tools provide an accessible way to see and understand trends, outliers, and patterns in data.
In the context of big data, data visualization becomes crucial. The sheer volume, velocity, and variety of big data make traditional analysis methods difficult. Visualization allows us to quickly grasp complex relationships within massive datasets, enabling faster and more effective decision-making.
Effective data visualizations transform numerical data into insightful visuals, making it easier to identify key insights and communicate findings to both technical and non-technical audiences.
Importance in Big Data Analysis
Data visualization plays a critical role in big data analysis. It provides a powerful mechanism to transform complex and massive datasets into understandable and actionable insights. Without effective visualization, the sheer volume and velocity of big data can overwhelm analysts, making it difficult to extract meaningful information.
Key benefits of data visualization in big data analysis include:
- Improved Understanding: Visual representations simplify complex data relationships, making them easier to grasp and interpret.
- Faster Insights: Visualizations enable analysts to quickly identify trends, patterns, and outliers that might otherwise be missed.
- Enhanced Communication: Visuals effectively communicate findings to both technical and non-technical audiences.
- Better Decision-Making: Data-driven insights gleaned from visualizations empower informed and strategic decision-making.
Through the use of charts, graphs, and other visual tools, data visualization unlocks the potential of big data, turning raw data into valuable knowledge.
Popular Visualization Tools
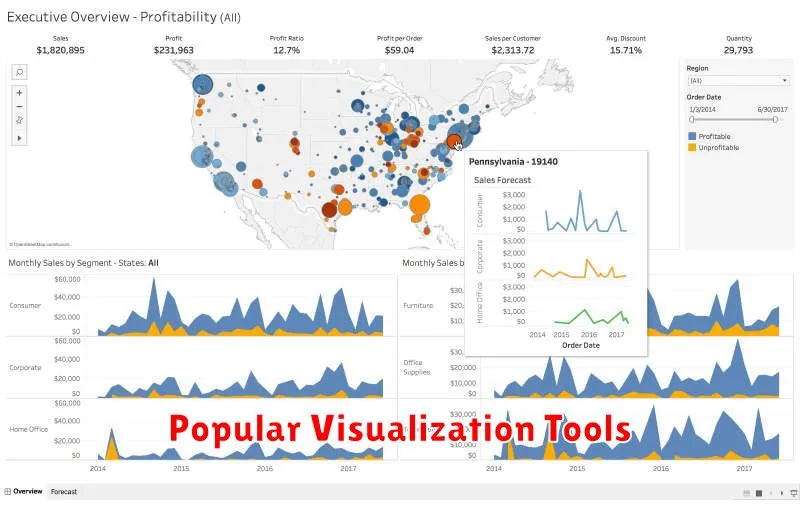
Several powerful tools have gained popularity for effectively visualizing big data. Choosing the right tool depends on the specific needs of your project, including the type of data, the desired visualizations, and the technical expertise of your team. Tableau and Power BI are favored for their user-friendly interfaces and robust business intelligence capabilities. They offer a wide range of visualization options and facilitate interactive dashboards. For more programming-centric approaches, Python libraries like Matplotlib and Seaborn provide extensive customization and flexibility for creating static, interactive, and animated visualizations.
D3.js, a JavaScript library, excels at producing dynamic and interactive web-based visualizations. It offers granular control over every aspect of the visual representation, making it suitable for highly customized solutions. Google Charts is another web-based option providing a user-friendly interface and a variety of chart types for embedding visualizations within web applications. Finally, for those working with large datasets requiring distributed processing, tools like Apache Superset offer scalability and integration with big data platforms.
Building Effective Dashboards
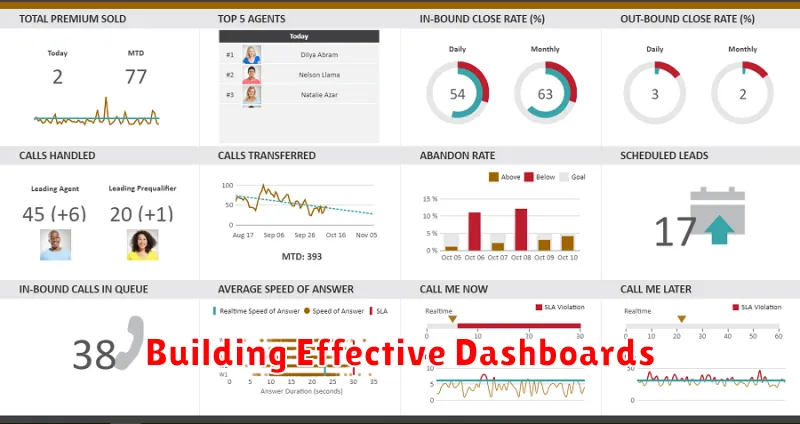
Dashboards serve as a central hub for visualizing key performance indicators (KPIs) and gaining actionable insights from data. A well-designed dashboard transforms complex data into easily digestible visuals, enabling informed decision-making.
Key considerations for building effective dashboards include:
- Purpose: Define the dashboard’s objective and target audience. What questions should it answer?
- Key Metrics: Select the most relevant KPIs to track and display. Prioritize metrics directly aligned with business goals.
- Visualizations: Choose appropriate chart types to effectively represent the data. Consider bar charts for comparisons, line charts for trends, and pie charts for proportions.
- Layout: Organize the dashboard logically to guide the viewer’s eye. Place the most important information prominently.
- Interactivity: Incorporate interactive elements like filters and drill-downs to allow users to explore the data further.
By adhering to these principles, you can create dashboards that effectively communicate data insights and empower stakeholders to make data-driven decisions.
Best Practices in Data Display
Effective data display is crucial for conveying insights from big data analysis. Following best practices ensures clear, accurate, and accessible communication.
Choose the right chart type. Different charts are suited for different data types and purposes. Bar charts excel at comparisons, line charts at trends over time, and scatter plots at correlations.
Simplify and declutter. Remove unnecessary elements like excessive gridlines, 3D effects, and distracting colors. Prioritize clarity over visual embellishments.
Label clearly and concisely. Provide informative titles, axis labels, and legends. Ensure labels are easy to read and understand.
Use appropriate scales and ranges. Scales should accurately represent the data without distortion. Avoid manipulating scales to exaggerate or downplay trends.
Consider your audience. Tailor your visualizations to the knowledge and experience of your target audience. Explain complex concepts clearly and provide context when necessary.
Choosing the Right Chart Type
Selecting the appropriate chart type is crucial for effective data visualization. The right chart can clearly communicate complex information, while the wrong one can obscure meaning and lead to misinterpretations. Consider the nature of your data and the message you want to convey when making your choice.
Key factors to consider include the type of data being visualized (categorical, numerical, time-series, etc.) and the relationship you want to highlight (comparison, distribution, composition, trend, etc.).
For comparing values, bar charts or column charts are effective. Distributions can be visualized with histograms or box plots. Pie charts and stacked bar charts are useful for showing composition. Line charts and area charts are best suited for displaying trends over time.
Careful consideration of these factors will ensure your chosen chart type effectively communicates the insights within your big data.