Cloud computing has revolutionized how we interact with technology, offering a flexible, scalable, and cost-effective alternative to traditional IT infrastructure. This article provides a comprehensive introduction to cloud computing for beginners, explaining its core concepts, benefits, and various service models. Whether you are a student, a business professional, or simply curious about this transformative technology, understanding cloud computing is increasingly essential in today’s digital world. We will demystify the complexities of cloud computing, breaking down technical jargon into easy-to-understand explanations, empowering you with the knowledge to navigate this rapidly evolving landscape.
From software as a service (SaaS) to platform as a service (PaaS) and infrastructure as a service (IaaS), we will explore the different ways businesses and individuals can leverage the cloud. This introductory guide will cover key topics such as cloud deployment models (public, private, and hybrid), cloud security considerations, and the advantages of adopting cloud-based solutions. By the end of this article, you will have a solid foundational understanding of cloud computing, enabling you to make informed decisions about how to utilize its power for personal or professional use.
What Is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of IT resources—everything from applications to data centers—over the Internet. Instead of owning, managing, and maintaining physical data centers and servers, you can access technology services, such as computing power, storage, and databases, on an as-needed basis from a cloud provider like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
Essentially, you’re renting these resources rather than owning them outright. This allows you to avoid the upfront costs and complexity of building and running your own IT infrastructure, and instead pay only for what you use.
Think of it like electricity. You don’t own a power plant to light your home; you simply plug into the grid and pay for the electricity you consume. Similarly, with cloud computing, you access the resources you need from a shared pool of resources managed by the cloud provider.
Benefits of Cloud vs Local Storage
Choosing between cloud and local storage depends on your specific needs. Cloud storage offers several advantages over traditional local storage.
Accessibility
Access your data from anywhere with an internet connection, enabling collaboration and remote work.
Scalability
Easily increase or decrease your storage capacity as needed, paying only for what you use. This flexibility is a key advantage over fixed local storage.
Cost-Effectiveness
Cloud storage eliminates the need for expensive hardware, software, and IT personnel, resulting in significant cost savings, especially for small businesses and individuals.
Data Recovery and Backup
Cloud providers typically offer robust data backup and recovery services, protecting your data against hardware failures, natural disasters, and accidental deletion.
Security
Reputable cloud providers invest heavily in security measures, potentially offering enhanced data protection compared to individual users or small businesses.
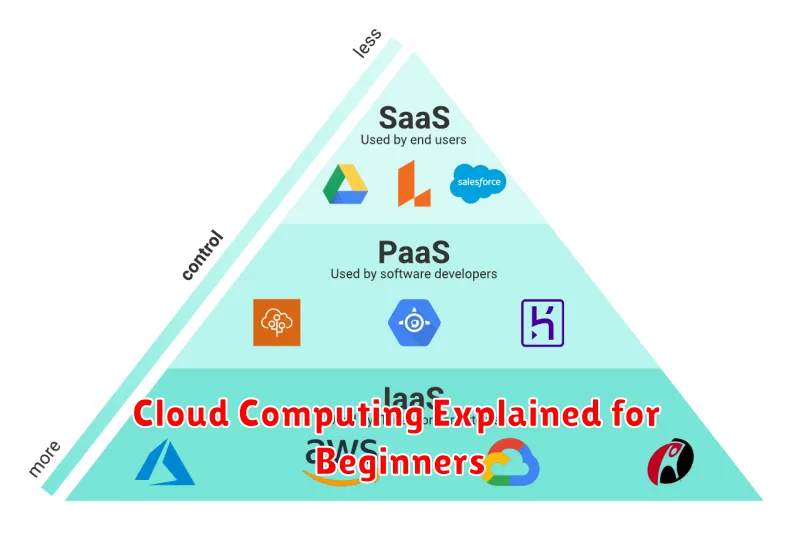
Types of Cloud Services (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS)
Cloud computing services are broadly categorized into three main types: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Each offers a different level of control and management responsibility.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides the foundational building blocks of cloud IT. Users gain access to computing resources like virtual machines, storage, and networks. This offers the most flexibility and control, requiring users to manage the operating system and applications themselves.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS offers a complete development and deployment environment in the cloud. It provides the platform for building, testing, and running applications without managing the underlying infrastructure. This allows developers to focus on coding and deployment.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS delivers ready-to-use software applications over the internet. Users access and use these applications without needing to install or manage any software or hardware. Common examples include email clients, customer relationship management (CRM) software, and office productivity suites.
Popular Cloud Providers

Several companies dominate the cloud computing market, offering a wide range of services to businesses and individuals. Understanding the strengths of each provider can help you make informed decisions about which platform best suits your needs. Here are a few of the most popular cloud providers:
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
AWS is the current market leader, boasting a comprehensive suite of services ranging from basic computing and storage to advanced machine learning and artificial intelligence. Their global infrastructure is extensive, providing high availability and reliability.
Microsoft Azure
Azure is a strong competitor to AWS, offering similar services with a focus on integration with existing Microsoft products. This makes it a popular choice for organizations already utilizing Microsoft’s ecosystem.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
GCP is known for its strong capabilities in data analytics and machine learning. Its competitive pricing and innovative services are attracting a growing number of users.
Common Use Cases

Cloud computing finds applications across diverse fields. Here are some common examples:
Data Storage and Backup
Cloud storage offers a scalable and cost-effective way to store and back up data. Users can access their files from anywhere with an internet connection.
Software Development and Testing
Developers utilize cloud platforms to build, test, and deploy applications rapidly. The cloud provides access to various development tools and environments without significant upfront investment.
Big Data Analytics
The cloud offers powerful tools and resources for processing and analyzing massive datasets. This enables businesses to gain valuable insights and make data-driven decisions.
E-commerce and Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Cloud-based e-commerce platforms and CRM systems provide businesses with the flexibility to scale their operations based on demand and manage customer interactions effectively.
Security in the Cloud
Security is a critical aspect of cloud computing. While cloud providers invest heavily in security measures, users also share responsibility for protecting their data and applications.
Cloud security is often described using the “shared responsibility” model. The cloud provider is responsible for the security of the cloud (the underlying infrastructure), while the customer is responsible for security in the cloud (their data and applications running on that infrastructure).
Key security concerns for cloud users include data breaches, data loss, and unauthorized access. Implementing strong passwords, using multi-factor authentication, and encrypting data are some of the essential security practices users should adopt.
Choosing the Right Service Model
A key aspect of cloud computing is selecting the appropriate service model. Cloud services are typically categorized into three main models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Each offers a different level of control and responsibility.
With IaaS, you manage the operating system, applications, and data, while the cloud provider manages the physical infrastructure like servers, networking, and storage. This offers the most control but also requires the most management.
PaaS provides a platform for developing and deploying applications. You manage the applications and data, but the cloud provider manages the underlying infrastructure and platform services. This simplifies development and deployment.
SaaS delivers ready-to-use software applications over the internet. The cloud provider manages everything, from the infrastructure to the application itself. This is the easiest to use but offers the least control.