In today’s interconnected digital landscape, cloud application security is paramount. Organizations increasingly rely on cloud apps for crucial operations, making robust security measures essential to protect sensitive data from evolving cyber threats. This article explores the must-have security features for cloud apps, providing valuable insights for businesses seeking to fortify their cloud infrastructure and mitigate risks. Understanding and implementing these crucial security features is no longer optional but a necessity for maintaining data integrity, ensuring business continuity, and fostering trust among stakeholders.
From access control and data encryption to vulnerability management and incident response, this guide will delve into the key elements that constitute a comprehensive cloud security strategy. Whether you’re migrating existing applications to the cloud or developing new cloud-native solutions, incorporating these essential security features from the outset is critical. By prioritizing cloud app security, organizations can confidently leverage the power of the cloud while safeguarding their valuable assets against the ever-present threat of cyberattacks. Learn about the must-have security features that will empower you to build a secure and resilient cloud environment.
The Importance of Cloud App Security
Cloud application security is paramount in today’s interconnected digital landscape. With businesses increasingly relying on cloud-based services for critical operations, protecting sensitive data and maintaining operational integrity is more crucial than ever. Failing to prioritize cloud app security can have severe consequences, including data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage.
Data breaches are a significant concern. Cloud apps often store vast amounts of sensitive data, making them attractive targets for cybercriminals. Robust security measures are essential to prevent unauthorized access and protect this valuable information.
Financial losses can result from various security incidents. Downtime caused by attacks can disrupt business operations, leading to lost revenue. Furthermore, the costs associated with incident response, recovery, and potential regulatory fines can be substantial.
Finally, reputational damage can be a long-lasting consequence of security failures. Loss of customer trust and negative publicity can significantly impact a business’s brand and future prospects.
Authentication and Access Control
Authentication verifies user identities before granting access to cloud resources. Strong authentication measures, like multi-factor authentication (MFA), are crucial. MFA requires users to provide multiple factors, such as a password and a one-time code, significantly enhancing security.
Access control defines what users can do within the cloud environment. Implementing the principle of least privilege ensures users only have access to the resources absolutely necessary for their roles. Role-based access control (RBAC) simplifies management by grouping users with similar permissions.
End-to-End Data Encryption
End-to-end encryption (E2EE) is a critical security feature that ensures only authorized parties can access sensitive data. With E2EE, data is encrypted on the sender’s device and remains encrypted until it reaches the intended recipient. This means that even the cloud provider cannot decrypt or access the data.
This robust approach protects data in transit and at rest, safeguarding against unauthorized access, data breaches, and surveillance. E2EE adds an extra layer of security, making it significantly more challenging for malicious actors to intercept and decipher sensitive information.
When evaluating cloud applications, prioritize those that offer robust E2EE implementation. This feature is essential for maintaining data confidentiality and integrity, particularly when dealing with sensitive information such as personal data, financial records, or intellectual property.
Secure APIs and Interfaces
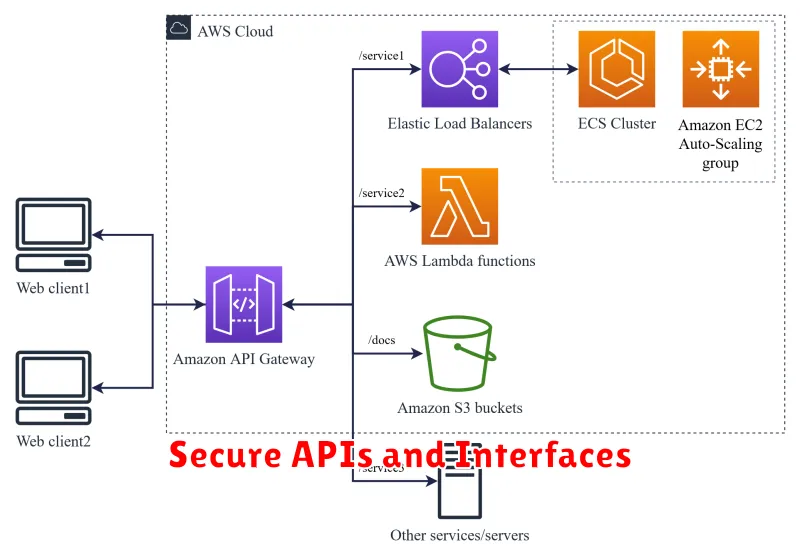
Secure application programming interfaces (APIs) and interfaces are paramount for cloud application security. APIs are the primary way cloud applications interact with each other, and unsecured APIs can be an easy entry point for attackers.
Key security measures for APIs and interfaces include robust authentication and authorization mechanisms. Strong authentication verifies the identity of the calling application or user, while authorization determines what actions they are permitted to perform. This can be achieved through methods such as API keys, OAuth 2.0, and JSON Web Tokens (JWT).
Input validation is crucial to prevent injection attacks. All incoming data through APIs and interfaces should be rigorously validated to ensure it conforms to expected formats and data types.
Regular security testing and vulnerability scanning of APIs and interfaces should be conducted to identify and address potential weaknesses before they can be exploited.
Regular Security Audits
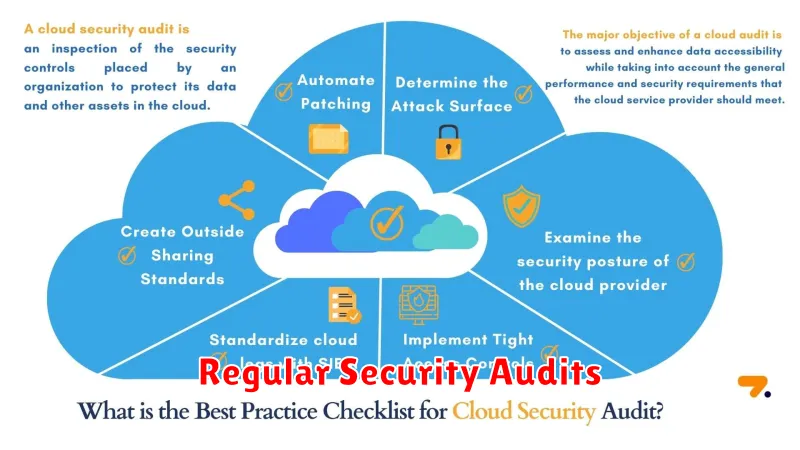
Regular security audits are essential for maintaining a strong security posture for cloud applications. These audits provide a comprehensive assessment of the application’s security controls, identifying vulnerabilities and areas for improvement.
Audits should encompass various aspects of security, including:
- Infrastructure Security: Evaluating the security of the underlying cloud infrastructure, such as network configurations and access controls.
- Application Security: Assessing the security of the application code itself, including vulnerability scanning and penetration testing.
- Data Security: Examining data protection measures like encryption, access control lists, and data loss prevention mechanisms.
- Compliance: Verifying adherence to relevant industry regulations and compliance standards.
The frequency of audits should be determined based on the sensitivity of the data being processed and the risk tolerance of the organization. Regular audits, whether conducted internally or by a third-party, provide valuable insights and contribute significantly to a robust cloud security strategy.
Disaster Recovery and Backup Plans
A robust disaster recovery (DR) plan is essential for any cloud application. This plan outlines the procedures to restore application functionality in the event of a disaster, such as a natural disaster, cyberattack, or hardware failure. A well-defined DR plan minimizes downtime and data loss, ensuring business continuity.
Key components of a DR plan include:
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO): The maximum acceptable downtime before recovery is complete.
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO): The maximum acceptable data loss in the event of a failure.
- Backup and restore procedures: Regular backups are crucial, with clearly defined processes for restoring data and applications.
- Failover mechanisms: Automated processes for switching to a backup system or location in case of a primary system failure.
Regularly testing the DR plan is vital to ensure its effectiveness and identify any gaps. This testing should simulate various disaster scenarios and validate the recovery process.

