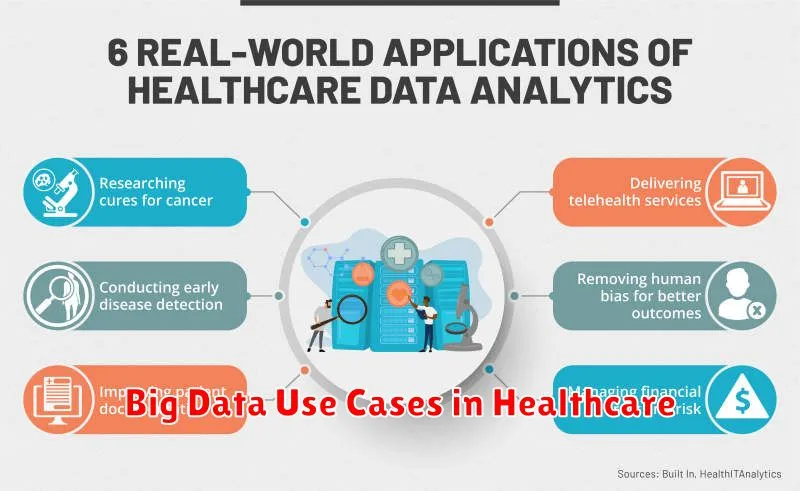
Big data is rapidly transforming the healthcare industry, offering unprecedented opportunities to improve patient care, streamline operations, and drive down costs. From predictive analytics for disease prevention to personalized medicine tailored to individual genetic profiles, the use cases of big data in healthcare are vast and constantly expanding. This article will explore some of the most impactful applications of big data analytics in healthcare, demonstrating how this technology is revolutionizing the delivery and management of healthcare services. Understanding the power of big data in healthcare is crucial for both providers and patients alike.
Delving into the specifics of big data use cases in healthcare, we will examine how big data is being leveraged to improve diagnostics, enhance treatment efficacy, and optimize resource allocation. Examples include using big data for real-time disease surveillance, developing innovative drug discovery protocols, and implementing data-driven population health management strategies. This exploration of big data in healthcare will highlight its transformative potential to address some of the most pressing challenges facing the healthcare industry today.
Overview of Big Data in Health
Big data in healthcare refers to the massive volumes of complex and varied data generated from various sources within the healthcare ecosystem. These sources include electronic health records (EHRs), medical imaging, wearable devices, pharmaceutical research, and genomic sequencing. The sheer volume, velocity, and variety of this data present both challenges and opportunities for improving patient care, optimizing operational efficiency, and advancing medical research.
The key characteristics of big data, often referred to as the “5 Vs,” are particularly relevant in the healthcare context. Volume refers to the massive amounts of data generated. Velocity describes the speed at which data is created and needs to be processed. Variety indicates the different formats of data, from structured data in databases to unstructured data like doctor’s notes. Veracity emphasizes the trustworthiness and quality of the data, a critical factor in healthcare decision-making. Finally, value highlights the potential insights and actionable knowledge that can be extracted from big data to improve outcomes.
Improving Diagnosis Accuracy
Big data plays a crucial role in enhancing the accuracy of medical diagnoses. By analyzing massive datasets of patient information, including medical history, lab results, imaging scans, and even genetic data, healthcare providers can gain deeper insights into individual cases. This data-driven approach allows for more precise and timely diagnoses, reducing the likelihood of misdiagnosis and improving patient outcomes.
Machine learning algorithms are particularly valuable in this context. These algorithms can be trained to identify complex patterns and correlations within patient data that may not be immediately apparent to human clinicians. This can lead to the early detection of diseases like cancer, allowing for earlier intervention and treatment.
Furthermore, big data analytics can help identify potential risk factors for specific diseases, enabling proactive interventions and preventative care. By identifying individuals at high risk, healthcare providers can implement targeted screening and monitoring programs, leading to better disease management and improved overall population health.
Predictive Analytics for Patients
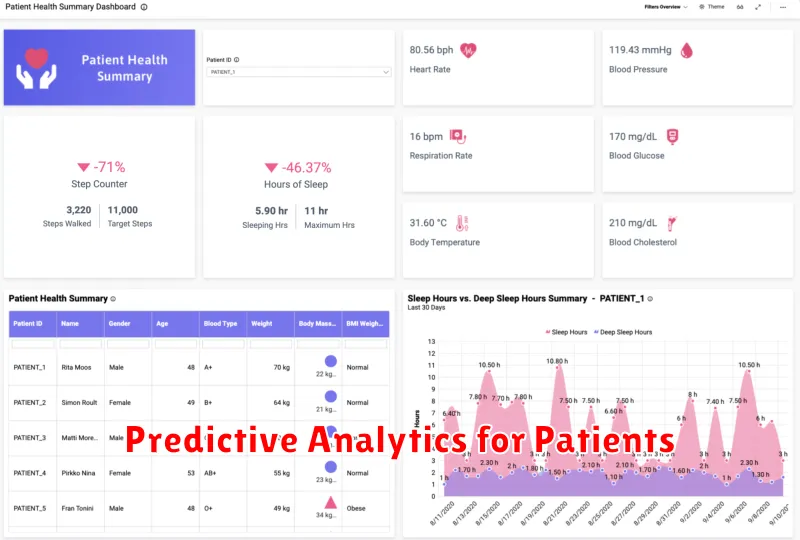
Predictive analytics plays a crucial role in enhancing patient care. By analyzing patient data, healthcare providers can forecast potential health risks and intervene proactively. This can lead to better patient outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
Several key applications benefit patients directly. Risk prediction models can identify individuals at high risk of developing chronic conditions like diabetes or heart disease. This allows for early intervention through lifestyle changes or preventive medication.
Personalized treatment plans can be developed based on individual patient characteristics and predicted responses to various therapies. This approach aims to optimize treatment efficacy and minimize adverse effects.
Predictive analytics can also forecast hospital readmissions, allowing for targeted interventions to support patients after discharge and reduce the likelihood of return visits.
Enhancing Hospital Operations
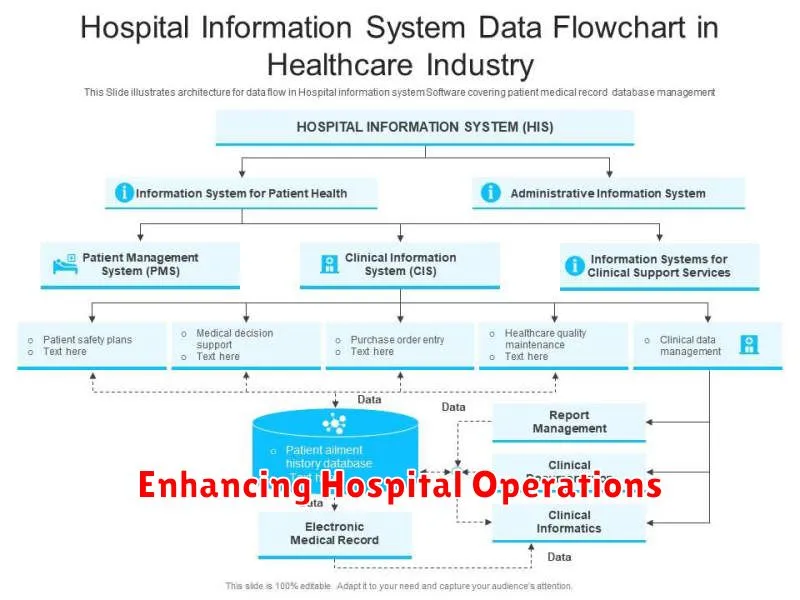
Big data analytics plays a crucial role in optimizing various hospital operations, leading to improved efficiency and patient care. Resource allocation is significantly enhanced by analyzing patient influx, staffing needs, and equipment utilization. This data-driven approach helps hospitals effectively manage resources, minimize delays, and reduce operational costs.
Predictive modeling enables hospitals to anticipate patient admissions and discharges, allowing for proactive bed management and optimized staffing levels. This minimizes wait times and improves patient flow throughout the hospital.
Operational cost reduction is another key benefit. Analyzing operational data can identify areas of inefficiency, allowing hospitals to streamline processes, reduce waste, and optimize resource utilization. This can lead to significant cost savings without compromising the quality of care.
Real-Time Health Monitoring
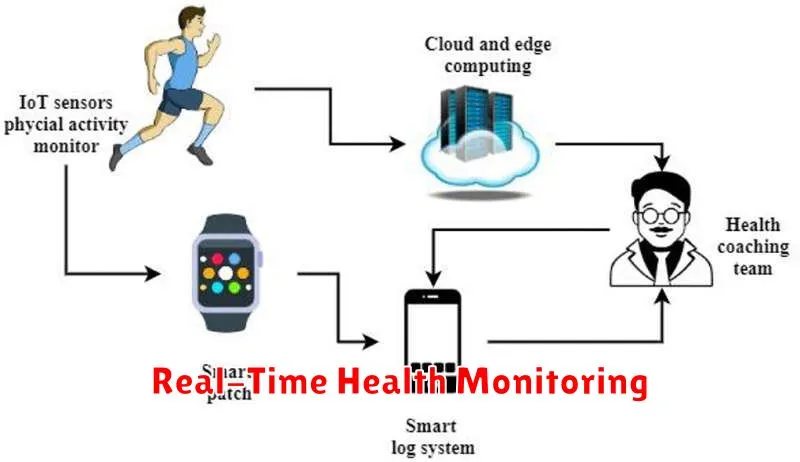
Real-time health monitoring leverages wearable sensors and connected devices to collect and analyze patient data continuously. This provides clinicians with up-to-the-minute insights into a patient’s physiological state, enabling proactive interventions and personalized care.
Conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and asthma can be monitored remotely, allowing for early detection of potential problems. This continuous stream of data empowers healthcare professionals to make data-driven decisions and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Key benefits include:
- Early detection of health deterioration: Allowing for timely interventions.
- Reduced hospital readmissions: Through continuous monitoring and proactive care.
- Improved patient outcomes: By facilitating personalized treatment plans.
- Enhanced patient engagement: Empowering patients to take control of their health.
Challenges in Data Privacy
Data privacy is a paramount concern in healthcare big data applications. The sensitive nature of patient information necessitates robust safeguards against unauthorized access and misuse.
One key challenge is de-identification. Removing identifying information while preserving data utility for analysis is complex. Techniques like pseudonymization and aggregation can help, but complete anonymization is often difficult to achieve without compromising research value.
Compliance with regulations like HIPAA adds another layer of complexity. Healthcare organizations must implement strict security measures and adhere to stringent data governance policies to avoid penalties and maintain patient trust.
The increasing use of cloud storage for big data also presents privacy risks. Ensuring data security and compliance within cloud environments requires careful consideration of data encryption, access controls, and vendor selection.
Patient consent and control over their data is another critical issue. Transparency about data usage and providing patients with options to manage their data are essential for building trust and fostering responsible data practices.