Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming numerous sectors, and education is no exception. The integration of AI in education promises to revolutionize how we teach and learn, offering personalized learning experiences, automated administrative tasks, and data-driven insights to enhance educational outcomes. This article explores the evolving role of AI in education, examining its potential benefits and challenges, and considering its impact on students, educators, and the future of learning.
From intelligent tutoring systems that adapt to individual student needs to AI-powered assessment tools that provide immediate feedback, the applications of artificial intelligence in education are diverse and expanding. Understanding the current capabilities and future potential of AI in education is crucial for stakeholders across the educational landscape. This article delves into the key areas where AI is making an impact, including personalized learning, automated grading and feedback, and the development of adaptive learning platforms, providing a comprehensive overview of this transformative technology’s role in shaping the future of education.
How AI Is Changing Classrooms
Artificial intelligence is rapidly transforming the educational landscape, impacting both how teachers teach and how students learn. Personalized learning is a key area of impact, with AI algorithms tailoring educational experiences to individual student needs and learning styles.
AI-powered tutoring systems can provide customized feedback and support, while intelligent learning platforms adapt to student progress, offering appropriate challenges and resources. This allows students to learn at their own pace and focus on areas where they need the most support.
Automation is another significant change. AI can automate time-consuming tasks for teachers, such as grading and administrative work, freeing up more time for personalized instruction and student interaction. AI-powered tools can also assess student work, identifying areas of strength and weakness.
Personalized Learning Experiences
AI is transforming education by enabling personalized learning experiences tailored to individual student needs. Traditional “one-size-fits-all” approaches often fail to address the diverse learning styles and paces within a classroom. AI algorithms can analyze student performance data, identifying strengths and weaknesses to create customized learning paths.
These personalized pathways can recommend specific learning resources, adjust the difficulty of exercises, and offer targeted feedback. This adaptive learning environment helps students learn at their own pace, focusing on areas where they require more support while accelerating their progress in areas where they excel.
For instance, AI-powered tutoring systems can provide individualized instruction and support, similar to a personal tutor. These systems can adapt to the student’s responses, offering hints, explanations, and additional practice as needed. This level of personalized attention can significantly enhance learning outcomes and boost student engagement.
Automated Grading Systems

Automated grading systems utilize artificial intelligence to evaluate student work, offering several potential advantages. These systems can process large volumes of assignments quickly, providing timely feedback to students and freeing up educators’ time for other tasks.
Currently, these systems are most effective for assessing objective assignments like multiple-choice tests and fill-in-the-blank exercises. However, advancements in natural language processing are enabling AI to evaluate more complex assignments, including essays and short-answer responses. This can potentially lead to more consistent grading and reduce subjectivity in evaluation.
While promising, automated grading systems also face challenges. Concerns exist regarding the systems’ ability to accurately assess higher-order thinking skills and creativity. Furthermore, ensuring fairness and addressing potential biases within the algorithms are crucial considerations for developers and educators.
AI Tutors and Virtual Assistants
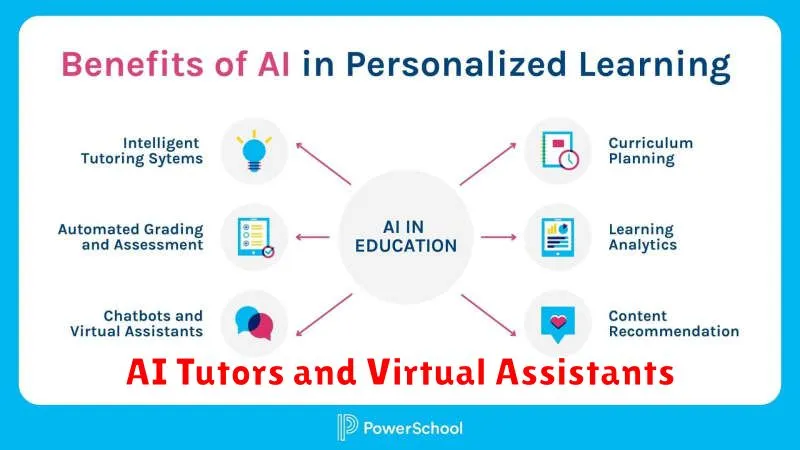
AI tutors offer personalized learning experiences, adapting to individual student needs and pacing. They can provide targeted instruction, feedback, and practice exercises in various subjects. These intelligent systems track student progress and identify areas requiring additional support, offering a tailored approach to education.
Virtual assistants, on the other hand, streamline administrative tasks and enhance communication. They can schedule meetings, send reminders, manage deadlines, and answer frequently asked questions. This frees up educators’ time, allowing them to focus on pedagogical tasks and student interaction. Virtual assistants can also facilitate communication between teachers, students, and parents, improving overall coordination and information flow.
Analyzing Student Performance
Artificial intelligence (AI) offers powerful tools for analyzing student performance, moving beyond traditional grading methods. AI algorithms can process vast amounts of data, identifying patterns and trends in student learning.
This analysis can pinpoint individual student strengths and weaknesses, enabling personalized learning interventions. For example, if a student consistently struggles with a particular concept, AI can recommend targeted exercises and resources to address that specific gap.
Furthermore, AI can analyze overall class performance, highlighting areas where the curriculum or teaching methods might need adjustment. This data-driven approach allows educators to make informed decisions about instructional strategies and resource allocation.
Ethical Concerns in EdTech
The integration of technology, particularly AI, within education raises several ethical considerations. Data privacy is paramount, with student data collection and usage requiring stringent safeguards. Concerns arise regarding who owns the data, how it’s secured, and potential misuse. Transparency in data handling practices is crucial.
Algorithmic bias is another key concern. AI systems trained on biased data can perpetuate and amplify existing inequalities. This bias can manifest in personalized learning platforms, assessment tools, and predictive analytics, potentially disadvantaging certain student groups.
The digital divide further exacerbates ethical challenges. Unequal access to technology and reliable internet connectivity can create learning disparities, limiting opportunities for students from marginalized communities.
Finally, the teacher’s role must be carefully considered. Over-reliance on technology could diminish the importance of human interaction and pedagogical expertise in the learning process. A balanced approach that leverages technology to enhance, not replace, effective teaching is essential.