Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are often used interchangeably, leading to confusion about their true meanings. This article clarifies the distinction between these two powerful technologies, explaining how they relate to one another and delving into their respective applications. Understanding the difference between AI and machine learning is crucial for anyone navigating the modern technological landscape. We will explore the core concepts of artificial intelligence and machine learning, highlighting their unique characteristics and demonstrating how ML serves as a subset of the broader field of AI.
While both artificial intelligence and machine learning aim to create intelligent systems, their approaches differ significantly. AI seeks to create systems that mimic human intelligence, encompassing a wide range of capabilities, from problem-solving and decision-making to natural language processing and computer vision. Machine learning, on the other hand, focuses on enabling systems to learn from data without explicit programming. By identifying patterns and insights within datasets, ML algorithms allow machines to improve their performance over time. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of these key distinctions, helping you understand the nuances of AI versus machine learning and their respective roles in shaping the future of technology.
Defining Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a broad field encompassing the development of computer systems capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence. These tasks include learning, problem-solving, decision-making, speech recognition, and visual perception.
At its core, AI aims to create machines that can mimic or even surpass human cognitive abilities. Different approaches exist for achieving this, ranging from rule-based systems to complex machine learning models. A key characteristic of AI is the ability to adapt to new information and improve performance over time.
Understanding Machine Learning
Machine learning, a subfield of artificial intelligence (AI), focuses on enabling computer systems to learn from data without explicit programming. Algorithms are designed to identify patterns, make predictions, and improve their performance over time based on the data they are exposed to.
Instead of relying on pre-defined rules, machine learning models learn from the provided data, building a model that can then be applied to new, unseen data. This learning process is typically iterative, with the model refining its parameters to minimize errors and improve accuracy.
There are several types of machine learning, including supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. Supervised learning uses labeled data to train models, while unsupervised learning deals with unlabeled data to discover underlying structures. Reinforcement learning focuses on training agents to make optimal decisions in an environment to maximize rewards.
Key Differences Explained
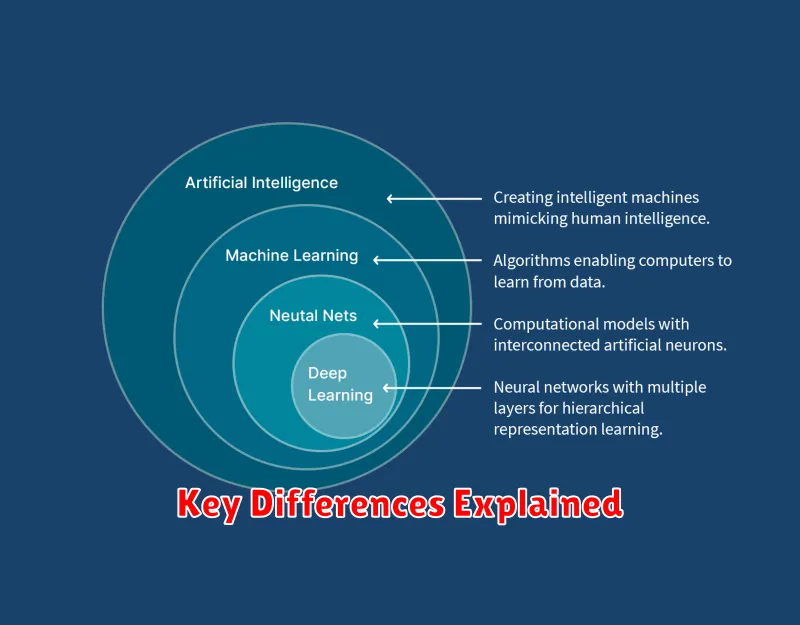
While the terms are often used interchangeably, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are distinct concepts. AI is the broader concept, encompassing any technique that enables computers to mimic human intelligence. This can include rule-based systems, expert systems, and machine learning.
Machine learning, on the other hand, is a specific subset of AI. It focuses on enabling computers to learn from data without explicit programming. Algorithms are trained on datasets, allowing them to identify patterns, make predictions, and improve their performance over time. In essence, machine learning provides the learning component within the larger field of artificial intelligence.
Think of it this way: AI is the overarching goal of creating intelligent machines, while machine learning is one specific technique used to achieve that goal. Other techniques, like deep learning (a subset of machine learning), also contribute to the broader field of AI.
Real-World Use Cases
Understanding the distinction between AI and machine learning is further clarified by examining real-world applications. While AI encompasses a broader range of functionalities, machine learning focuses specifically on enabling systems to learn from data.
Artificial Intelligence
AI is employed in diverse applications, including:
- Gaming: AI powers non-player characters (NPCs) and provides dynamic game adjustments.
- Robotics: AI enables robots to navigate complex environments and perform intricate tasks.
- Expert Systems: AI systems can emulate human expertise in fields like medicine and finance.
Machine Learning
Machine learning is used for tasks such as:
- Spam Filtering: Algorithms learn to identify and filter unwanted email messages.
- Fraud Detection: Machine learning models detect fraudulent transactions in real-time.
- Personalized Recommendations: E-commerce platforms use machine learning to suggest products based on user behavior.
Which One to Learn First?
Deciding whether to delve into artificial intelligence (AI) or machine learning (ML) first depends on your career goals and learning style. If you’re interested in the broad concepts of intelligent systems, AI offers a good starting point. It provides an overview of various AI subfields, including ML, natural language processing, and computer vision.
However, if you prefer a more hands-on, practical approach, beginning with machine learning is often recommended. ML provides the foundational tools and techniques used to build many AI systems. A strong understanding of ML algorithms and data manipulation is crucial for implementing and deploying effective AI solutions. Learning ML first equips you with the practical skills needed to create intelligent applications, paving the way for deeper exploration of specific AI domains later.
Future Trends and Careers
The fields of AI and machine learning are rapidly evolving, promising exciting future trends and diverse career opportunities. Explainable AI (XAI) is gaining traction, focusing on making AI decision-making more transparent and understandable. This is crucial for building trust and ensuring responsible AI deployment.
Edge computing, which processes data closer to its source, is another significant trend. It allows for faster processing and reduced latency, paving the way for more real-time AI applications. Furthermore, the increasing need for AI model security and robustness is driving research and development in areas like adversarial training and anomaly detection.
The demand for skilled professionals in these fields is also surging. AI specialists, machine learning engineers, data scientists, and AI ethicists are just a few examples of in-demand roles. As AI becomes increasingly integrated into various industries, the need for professionals who can develop, implement, and manage these technologies will continue to grow.