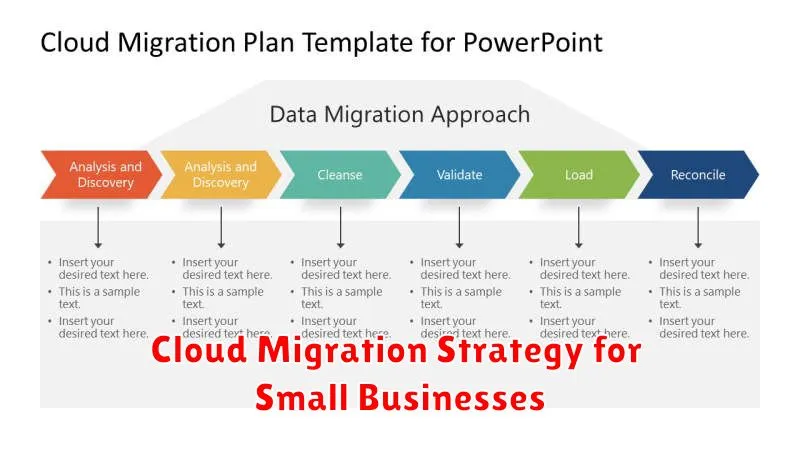
Migrating to the cloud can be a game-changer for small businesses. A well-defined cloud migration strategy offers numerous advantages, including cost savings, increased scalability, and enhanced security. This article will provide a comprehensive guide for small businesses looking to transition their operations to the cloud. We will cover key considerations, best practices, and potential challenges to help you develop a successful cloud migration strategy tailored to your specific needs. Understanding the different cloud migration types, such as lift and shift, rehosting, and refactoring, is crucial for maximizing the benefits of cloud computing.
Developing a robust cloud migration strategy is essential for minimizing disruptions and ensuring a seamless transition. This article will delve into the critical steps involved, from assessing your current IT infrastructure to selecting the right cloud provider and managing post-migration optimization. We’ll explore the importance of data security, disaster recovery, and compliance in your cloud migration plan. By following the outlined strategies, small businesses can leverage the power of the cloud to drive innovation, streamline operations, and achieve sustainable growth.
Why Migrate to the Cloud?
Migrating to the cloud offers small businesses a variety of compelling advantages. Cost savings are a primary driver, eliminating the need for expensive hardware, software licenses, and IT staff. Cloud solutions offer flexible, pay-as-you-go pricing models, allowing businesses to scale resources up or down as needed, paying only for what they use.
Enhanced security is another key benefit. Reputable cloud providers invest heavily in security measures that often surpass what small businesses can afford individually. Cloud services also offer improved data backup and disaster recovery capabilities, ensuring business continuity in the event of unforeseen circumstances.
Furthermore, the cloud facilitates increased collaboration amongst employees, particularly with remote work becoming increasingly prevalent. Cloud-based applications and data accessibility promote teamwork and productivity from anywhere with an internet connection.
Finally, cloud migration allows for greater flexibility and scalability. Businesses can easily adjust their computing resources to meet changing demands, enabling rapid growth and adaptation to market dynamics without significant capital investment.
Planning Your Cloud Roadmap
A well-defined roadmap is crucial for a successful cloud migration. This roadmap should outline the steps, timelines, and resources required for each phase of the migration.
Start by assessing your current IT infrastructure and identifying applications suitable for cloud migration. Prioritize applications based on business needs and complexity.
Next, select a suitable cloud deployment model (public, private, or hybrid) and a cloud provider that aligns with your business requirements and budget. Consider factors like security, scalability, and support.
Develop a detailed migration plan outlining the specific steps for each application, including data migration, testing, and cutover. Establish clear timelines and allocate necessary resources for each phase.
Choosing the Right Provider
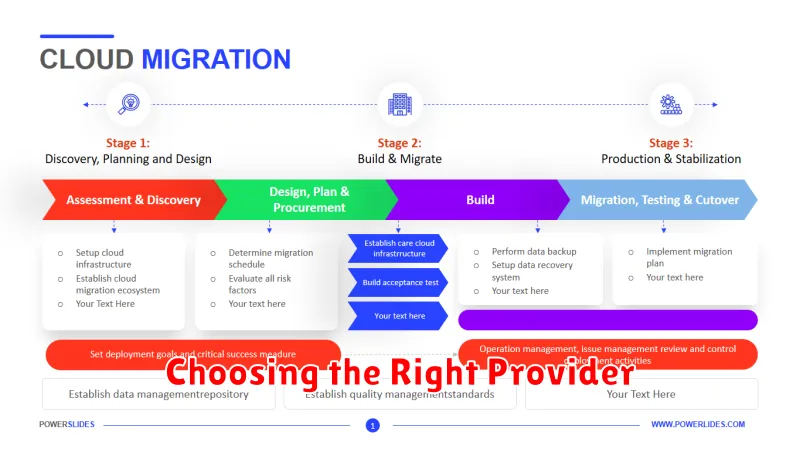
Selecting the right cloud provider is a critical step in your cloud migration strategy. Several factors should influence your decision. Consider your specific business needs, including required storage, computing power, and security requirements.
Cost is another crucial factor. Compare pricing models from different providers, paying close attention to potential hidden costs. Don’t simply opt for the cheapest option; ensure the provider offers the features and support your business requires.
Scalability is also important. Choose a provider that can easily accommodate your future growth. Evaluate their ability to scale resources up or down as needed.
Finally, consider the provider’s reputation and support. Look for a provider with a proven track record of reliability and excellent customer support. A responsive support team can be invaluable during the migration process and beyond.
Steps to Move Data Securely
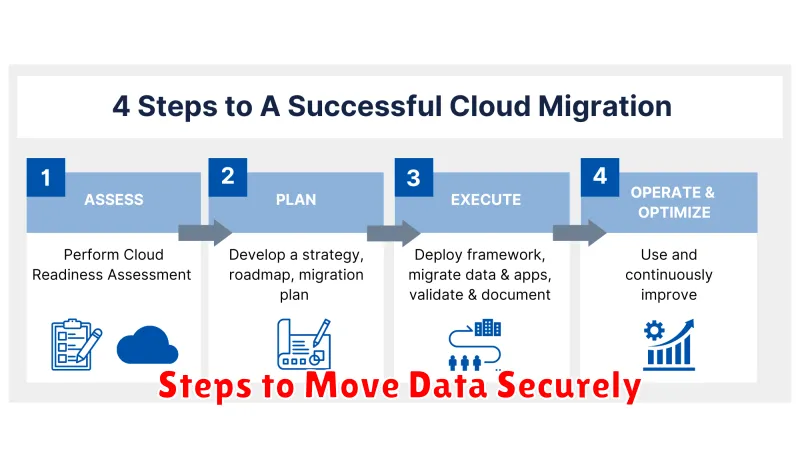
Securely migrating data to the cloud requires careful planning and execution. Data security should be the top priority throughout the entire process.
Discovery and Assessment: Start by identifying all sensitive data and classifying it according to its sensitivity level. This helps determine the appropriate security measures needed.
Choose a Secure Cloud Provider: Select a provider that offers robust security features such as encryption, access controls, and compliance certifications relevant to your industry.
Data Encryption: Encrypt data both in transit and at rest. Use strong encryption algorithms and manage encryption keys securely.
Validation and Testing: Thoroughly test the migration process and validate data integrity after the migration is complete. Ensure all security measures are functioning correctly.
Training Your Team on New Tools
A successful cloud migration requires your team to be proficient with the new tools and platforms. Training is a crucial element of this process. Inadequate training can lead to frustration, decreased productivity, and security risks.
Identify the key tools your team will be using in the cloud environment. This might include new software applications, cloud management consoles, or collaboration platforms.
Consider various training methods. Instructor-led training, online tutorials, and hands-on practice are all effective options. Choose the method, or combination of methods, that best suits your team’s learning styles and the complexity of the tools.
Prioritize training on security best practices for the cloud environment. This includes password management, access control, and data protection protocols.
Allocate sufficient time for training and ensure that all team members can participate. This investment will pay off in the long run by facilitating a smoother transition and maximizing the benefits of the cloud.
Monitoring and Optimization
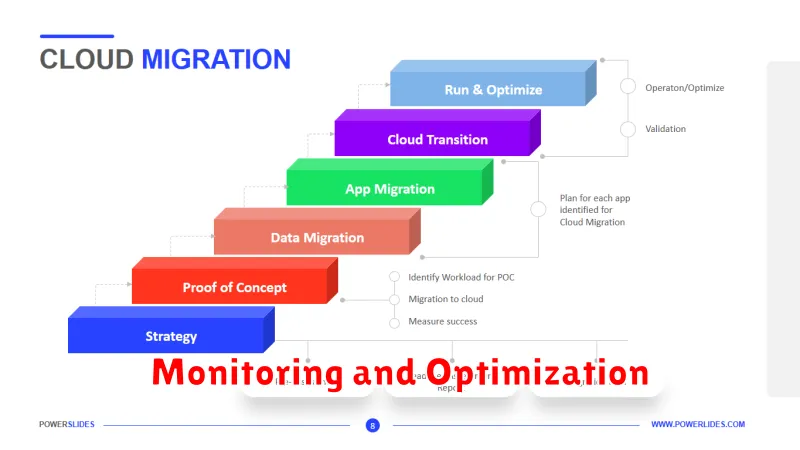
After migration, continuous monitoring is crucial. This involves tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) like uptime, latency, and resource utilization. Cloud providers offer various monitoring tools that provide real-time insights into your cloud environment.
Optimization is an ongoing process. Analyze the performance data gathered through monitoring to identify areas for improvement. This might include right-sizing virtual machines, optimizing database queries, or leveraging serverless computing.
Regularly review your cloud spending to ensure cost-efficiency. Cloud providers offer cost management tools that help identify areas where you can reduce costs, such as eliminating unused resources or taking advantage of reserved instances.