Quantum computing represents a paradigm shift in computational power, harnessing the principles of quantum mechanics to solve complex problems beyond the capabilities of classical computers. Unlike classical computers that rely on bits representing 0 or 1, quantum computers utilize qubits. These qubits leverage superposition and entanglement, allowing them to exist in multiple states simultaneously. This fundamental difference enables quantum computers to explore vast computational spaces and tackle problems in fields like medicine, materials science, and cryptography, which are intractable for even the most powerful classical supercomputers. Understanding the basics of quantum computing is crucial to grasping the transformative potential of this cutting-edge technology.
This article delves into the core concepts of quantum computing, explaining what it is and how it works. We’ll explore the fundamental principles of superposition, entanglement, and quantum algorithms, providing a clear and concise overview of this revolutionary field. We will also examine the potential applications of quantum computing and the challenges facing its development. By the end of this article, you will have a foundational understanding of quantum computing, its potential impact, and the ongoing research driving its advancement. Join us as we unlock the mysteries and explore the immense possibilities of the quantum realm.
Understanding Quantum Computing
Quantum computing represents a paradigm shift in computation, leveraging the principles of quantum mechanics to solve complex problems beyond the capabilities of classical computers. Unlike classical computers that store information as bits representing 0 or 1, quantum computers utilize qubits. Qubits leverage superposition and entanglement, enabling them to represent 0, 1, or a combination of both simultaneously.
Superposition allows a qubit to exist in multiple states at once, vastly increasing computational power. Entanglement links two or more qubits together, so they share the same fate, even when separated. This interconnectedness allows for complex calculations to be performed exponentially faster than on classical systems.
While still in its nascent stages, quantum computing holds immense potential across various fields. From drug discovery and materials science to financial modeling and cryptography, the ability to tackle previously intractable problems promises transformative advancements.
Key Differences from Classical Computing
Quantum computing diverges from classical computing in several fundamental ways. Classical computers store information as bits representing 0 or 1. Quantum computers leverage qubits. Qubits utilize quantum mechanical phenomena like superposition, allowing them to represent 0, 1, or a combination of both simultaneously.
Another key difference lies in how computations are performed. Classical computers process information sequentially using logic gates. Quantum computers employ quantum gates to manipulate qubits and perform computations, exploiting entanglement. Entanglement links two or more qubits, allowing them to share the same fate regardless of distance, enabling parallel processing and potentially exponential speedups for certain tasks.
Quantum Bits (Qubits) Explained
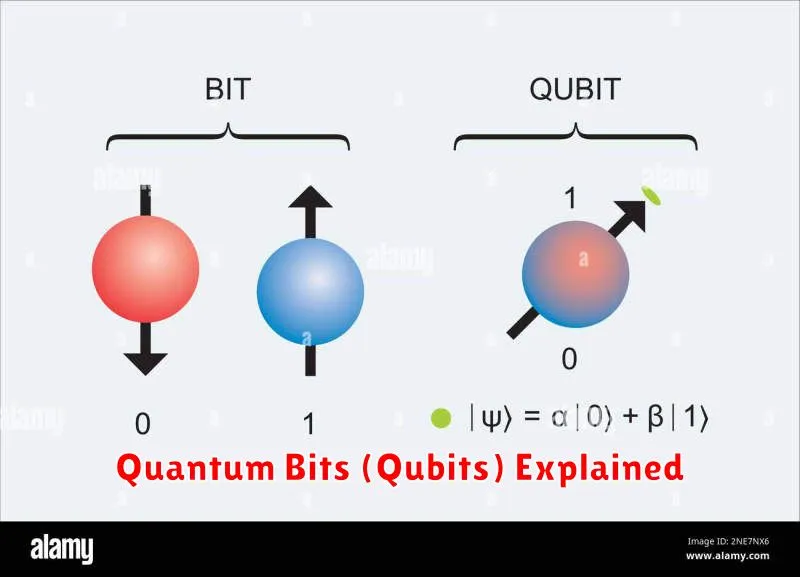
At the heart of quantum computing lies the qubit, the quantum analog of the classical bit. While classical bits represent information as either 0 or 1, qubits leverage the principles of quantum mechanics to exist in a superposition. This means a qubit can represent 0, 1, or a combination of both simultaneously.
This unique capability is enabled by two key quantum phenomena: superposition and entanglement. Superposition allows a qubit to exist in multiple states at once, vastly increasing computational power. Entanglement links two or more qubits together, so that they share the same fate, even when separated by large distances. Measuring the state of one entangled qubit instantly reveals the state of the others.
These properties allow quantum computers to explore numerous possibilities simultaneously, making them potentially capable of solving complex problems that are intractable for even the most powerful classical computers.
Real-World Applications of Quantum Tech
While still in its nascent stages, quantum technology promises revolutionary advancements across various sectors. One prominent application lies in drug discovery and development. Quantum computers can simulate molecular interactions with unprecedented accuracy, accelerating the identification of promising drug candidates and optimizing existing treatments. This capability has the potential to dramatically reduce development time and costs, ultimately leading to more effective therapies.
Materials science is another area ripe for disruption. Quantum simulations can predict the properties of new materials, enabling researchers to design compounds with specific characteristics, such as enhanced strength, conductivity, or durability. This could revolutionize industries ranging from electronics to aerospace.
Financial modeling stands to benefit significantly from quantum computing. Complex algorithms can be used to optimize investment portfolios, assess risk more accurately, and develop sophisticated trading strategies. This improved computational power could lead to more stable and efficient financial markets.
Finally, cryptography faces both a challenge and an opportunity with the rise of quantum computing. Existing encryption methods are vulnerable to attacks from sufficiently powerful quantum computers. However, quantum cryptography offers the potential for unbreakable encryption, ensuring secure communication in the future.
Challenges in Development
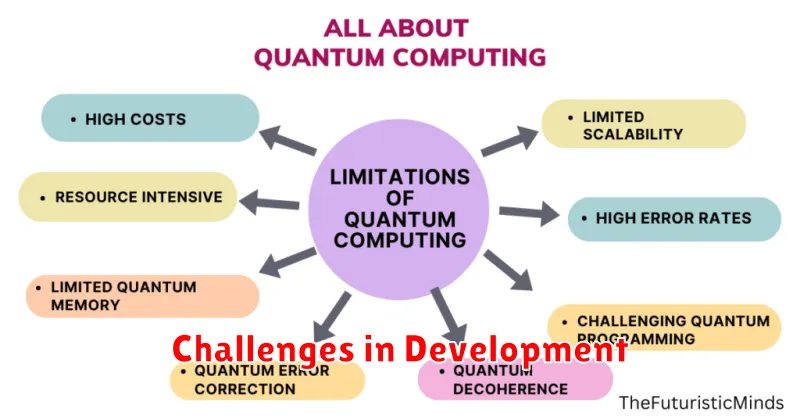
Quantum computing, while promising, faces significant hurdles in its development. One key challenge is scalability. Building systems with a sufficient number of qubits to tackle complex problems is incredibly difficult. Current quantum computers are limited in size, hindering their practical applications.
Qubit stability presents another major obstacle. Qubits are extremely fragile and prone to decoherence, losing their quantum properties quickly. Maintaining their coherence for extended periods is crucial for performing complex computations.
Error correction is also a significant concern. Quantum computations are susceptible to errors, and robust error correction mechanisms are essential for reliable results. Developing efficient and scalable error correction techniques is an ongoing research area.
Finally, the development of quantum algorithms and software is still in its nascent stages. Creating algorithms that effectively leverage the power of quantum computers requires specialized expertise and poses a significant challenge.
Companies Leading the Innovation
Several companies are at the forefront of quantum computing development, pushing the boundaries of this nascent technology. These companies are investing heavily in research and development, building both hardware and software solutions.
IBM is a prominent player, having developed quantum processors accessible through the cloud. They are actively working on improving qubit coherence times and scaling up their quantum systems. Google is another key player, known for their research on quantum supremacy. Their focus lies in developing fault-tolerant quantum computers.
Other notable companies contributing to the advancement of quantum computing include Rigetti Computing, specializing in superconducting qubit technology, and IonQ, focusing on trapped ion quantum computers. D-Wave Systems offers a different approach with their quantum annealing machines, designed for specific optimization problems.

