In today’s increasingly interconnected world, remote work has become more prevalent than ever. While this offers numerous benefits for both employees and employers, it also presents unique cybersecurity challenges. Protecting sensitive data and systems is paramount, especially when employees access company resources from various locations and networks. This necessitates a heightened awareness of cybersecurity threats and the implementation of robust cybersecurity practices. This article will provide essential cybersecurity tips for remote workers to help safeguard valuable information and maintain a secure working environment. Understanding and applying these tips is crucial for individuals and organizations alike to mitigate the risks associated with remote work.
From securing home networks with strong passwords and firewalls to recognizing and avoiding phishing scams and other cyber threats, remote workers play a vital role in maintaining a strong security posture. This article will cover key aspects of remote work security, including best practices for password management, data protection, device security, and the use of Virtual Private Networks (VPNs). By following these cybersecurity tips, remote workers can contribute to a more secure digital workspace and protect themselves and their organizations from potentially devastating cyberattacks. We will explore practical steps that are easy to implement and can significantly enhance cybersecurity for remote workers.
Why Remote Work Increases Risk
The shift to remote work has significantly broadened the attack surface for cybercriminals. Home networks often lack the sophisticated security infrastructure of corporate environments, making them more vulnerable to intrusion. Employees utilizing personal devices may not have the same level of security software or updates as company-managed equipment.
Blurred lines between personal and professional use on these devices further exacerbate the risk. Downloading files, clicking on phishing links, or accessing unsecured websites on a device also used for work creates potential entry points for malware and other threats.
The decentralized nature of remote work also presents challenges. Managing and monitoring security across numerous dispersed locations and networks is inherently more complex than within a centralized office setting. This difficulty can make it harder to identify and respond to security breaches promptly.
Secure Your Network Connections
Protecting your network connections is paramount when working remotely. Using unsecured networks exposes your data to potential threats. Always prioritize secure connections.
Use a Virtual Private Network (VPN). A VPN creates a secure, encrypted connection over a public network, shielding your online activity from prying eyes. This is especially critical when using public Wi-Fi.
Secure your home network. Use a strong password for your Wi-Fi router and enable firewall protection. Regularly update your router’s firmware to patch security vulnerabilities.
Be cautious of public Wi-Fi. Limit sensitive activities like online banking or accessing confidential work data when connected to public Wi-Fi, even when using a VPN. Public networks are inherently less secure.
Using VPNs and Firewalls
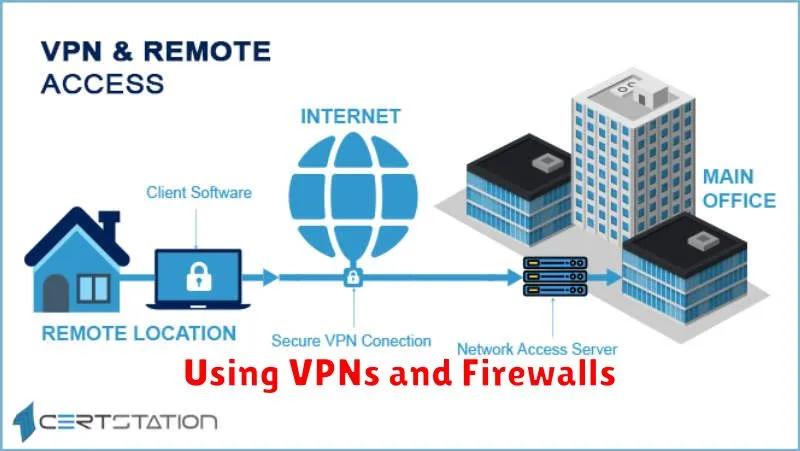
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) and firewalls are essential tools for remote workers. They add layers of security to protect your data and devices when connecting to the internet, especially on public Wi-Fi.
VPNs
A VPN creates a secure, encrypted connection between your device and a remote server. This protects your data from being intercepted by third parties. It also masks your IP address, adding a layer of anonymity and making it harder for websites and online services to track your activity. When working remotely, always use a reputable VPN, especially when handling sensitive company data.
Firewalls
Firewalls act as a barrier between your device and the internet, blocking unauthorized incoming and outgoing network traffic. They examine data packets and determine whether they should be allowed through based on pre-configured rules. Maintaining a robust firewall, whether software-based or hardware-based, is crucial for blocking malicious attacks and protecting your system.
Password Managers and Authentication
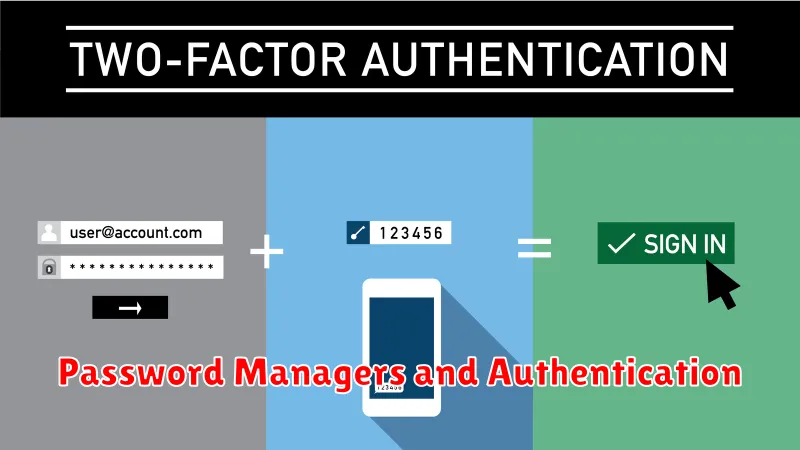
Strong passwords are fundamental to online security. Using unique, complex passwords for each account is crucial, but remembering them all can be challenging. This is where password managers come in. These tools securely store and generate strong passwords, eliminating the need to memorize them. They also often include features like breach detection, alerting you if your credentials are compromised.
Beyond passwords, multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security. MFA requires at least two factors to verify your identity. These factors typically fall into three categories: something you know (like a password), something you have (like a security token or smartphone), and something you are (like a fingerprint). Enabling MFA whenever possible significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if your password is compromised.
Avoiding Phishing Scams
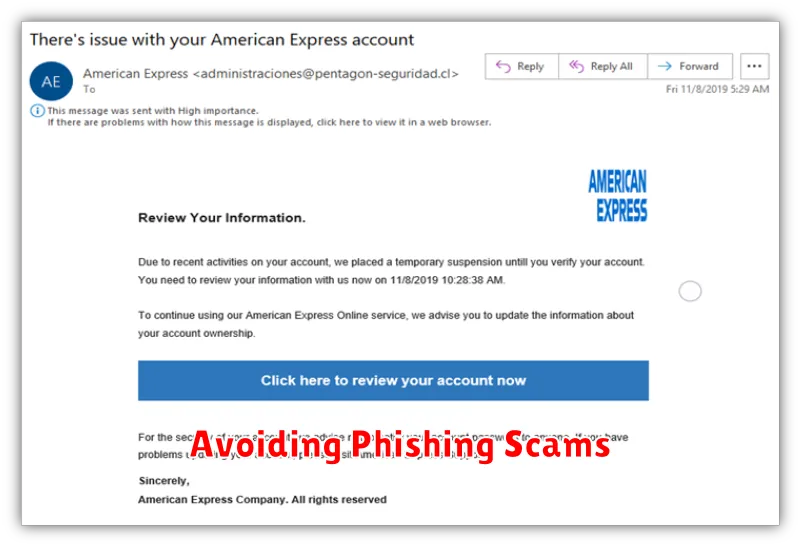
Phishing attacks are a significant threat to remote workers. These scams use deceptive emails, messages, or websites to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information like usernames, passwords, or credit card details.
Recognize phishing attempts by looking for suspicious signs. Check the sender’s email address for inconsistencies, be wary of generic greetings, and avoid clicking on links or attachments from unknown sources. Hover over links to see the actual URL, and if it looks suspicious, don’t click it.
Verify requests for information. If you receive an email asking for login credentials or personal data, contact the organization directly through a known phone number or website. Do not reply to the suspicious email.
Report suspected phishing attempts to your IT department or security team. Prompt reporting helps protect yourself and others from falling victim to these scams.
Regular Software Updates
One of the most critical aspects of cybersecurity for remote workers is maintaining up-to-date software. Outdated software often contains vulnerabilities that cybercriminals can exploit to gain access to your systems. Regularly updating your operating system, applications, and browser plugins is essential to patch these security flaws.
Enable automatic updates whenever possible. This ensures you receive and install the latest security patches without delay. For software that doesn’t offer automatic updates, schedule regular checks for new versions and promptly install them.
This proactive approach significantly reduces your risk of becoming a victim of cyberattacks.

