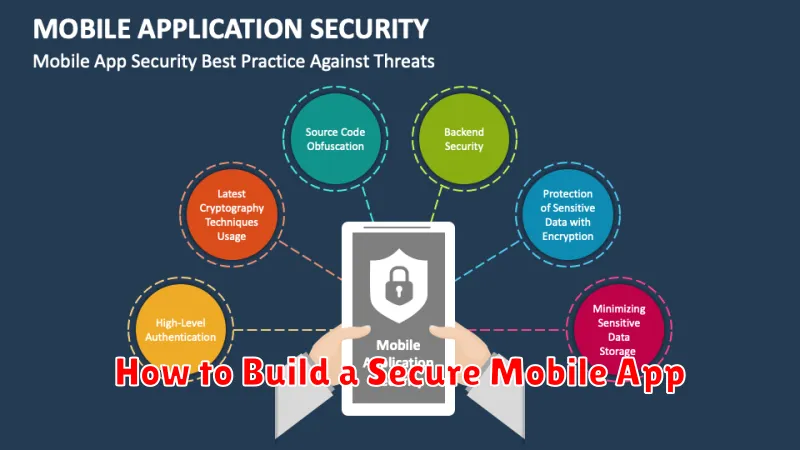
In today’s interconnected world, mobile applications have become integral to our daily lives. From banking and shopping to communication and entertainment, we rely on mobile apps for a multitude of tasks. This reliance, however, necessitates a strong emphasis on security. Building a secure mobile app is no longer a luxury, but a critical requirement to protect sensitive user data from malicious actors. This article will delve into the essential steps and best practices for building a secure mobile app, covering key aspects such as secure design principles, data encryption, authentication, and vulnerability testing.
Developing a secure mobile app requires a proactive and comprehensive approach throughout the entire development lifecycle. By understanding potential security threats and implementing robust security measures, developers can create apps that instill user trust and safeguard valuable information. This guide will provide practical advice and actionable insights to help you build secure mobile apps that are resilient against the ever-evolving landscape of mobile security threats. Whether you are developing for iOS or Android, the principles and techniques discussed herein will equip you with the knowledge to fortify your mobile app security.
Understanding Mobile Security Basics
Mobile security is paramount in today’s interconnected world. Protecting sensitive user data is a crucial responsibility for app developers. This involves understanding potential threats and implementing appropriate security measures throughout the app development lifecycle.
Key areas to consider include data storage, transmission, and authentication. Data at rest should be encrypted using robust algorithms. Data in transit requires secure communication protocols like HTTPS. Strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication, should be employed to verify user identities.
Platform-specific security guidelines also play a vital role. Whether developing for iOS or Android, adhering to platform best practices strengthens the overall security posture of the app. Regular security audits and penetration testing further help identify and mitigate vulnerabilities.
Implementing Secure Login Systems
Secure authentication is crucial for protecting user data and maintaining the integrity of your mobile application. Employing robust login systems helps prevent unauthorized access and safeguards sensitive information.
Consider using multi-factor authentication (MFA). MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity through multiple channels. This might include a password combined with a one-time code sent via SMS or email, or biometric verification.
Password management is another critical aspect. Enforce strong password policies, requiring a minimum length, a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Never store passwords in plain text. Instead, use a strong, one-way hashing algorithm like bcrypt or Argon2 to store password hashes securely.
Implement secure session management. After successful authentication, issue a unique session token to the user. This token should be stored securely on the device and used for subsequent API calls. Implement token expiration and renewal mechanisms to mitigate the risk of unauthorized access if a token is compromised.
Data Encryption Best Practices

Data encryption is crucial for protecting sensitive information within your mobile app. Employing robust encryption methods ensures data confidentiality and integrity, safeguarding it from unauthorized access.
Encryption at Rest: Protect stored data by encrypting databases and files. Use strong encryption algorithms like Advanced Encryption Standard (AES-256). Secure the encryption keys carefully, avoiding storage alongside the encrypted data.
Encryption in Transit: Secure data transmission between the app and the server using HTTPS with TLS 1.3 or later. This encrypts the communication channel, protecting against man-in-the-middle attacks.
Key Management: Proper key management is fundamental. Implement a secure system for generating, storing, and rotating encryption keys. Consider using a hardware security module (HSM) for enhanced key protection.
Platform-Specific Considerations: Leverage platform-provided security features like the Android Keystore System and Apple’s Keychain for secure key storage and cryptographic operations.
Preventing Common Vulnerabilities

Building a secure mobile application requires proactive measures to prevent common vulnerabilities. Input validation is crucial. Every piece of data entering the app must be checked for proper format and type to prevent injection attacks.
Secure data storage is another key aspect. Sensitive information, such as user credentials and personal data, should be encrypted both in transit and at rest. Consider using platform-provided secure storage mechanisms or established encryption libraries.
Authentication and authorization must be robust. Implement strong password policies and multi-factor authentication where appropriate. Clearly define and enforce access controls to limit what users can do within the app.
Regular security testing, including penetration testing and code reviews, helps identify and address vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. Staying updated with the latest security best practices and platform updates is essential for maintaining a strong security posture.
Using Trusted Libraries and APIs

Leveraging well-established and reputable libraries and APIs is crucial for building secure mobile applications. Trusted libraries often undergo rigorous security testing and have established vulnerability disclosure processes, reducing the risk of introducing known weaknesses into your app.
When selecting libraries, prioritize those with active maintenance, a strong community, and clear documentation. Thoroughly vet the library’s permissions and ensure they align with your app’s functionality. Avoid outdated or unmaintained libraries, as they can be susceptible to known exploits.
Similarly, integrating with trusted APIs is essential. Verify the API provider’s security practices and data handling policies. Implement proper authentication and authorization mechanisms to protect data exchanged between your app and the API.
Testing with Security Tools
Employing security testing tools is crucial for identifying vulnerabilities within your mobile application. These tools automate various tests, saving time and resources while providing comprehensive coverage.
Static Application Security Testing (SAST) analyzes the source code without executing the application. It helps detect flaws like SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS). Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST), conversely, tests the running application to identify vulnerabilities like authentication and authorization issues, as well as server-side injection flaws.
Mobile Application Security Testing (MAST) tools cater specifically to mobile platforms, addressing vulnerabilities related to the mobile operating system, insecure data storage, and weak cryptography.
Consider incorporating penetration testing (pentesting) to simulate real-world attacks. Professional penetration testers can uncover vulnerabilities that automated tools may miss. This provides a valuable perspective on how a malicious actor might exploit weaknesses in your app.